Poultry Processing Industry eTool
Tasks » Receiving & Killing
The receiving and killing operation is a largely automated process in most poultry plants and includes receiving live birds, killing, scalding, defeathering, and removing feet. This operation includes the following tasks:
- Task 1: Forklift Operator: Moves the poultry cages from trucks to conveyor/dumping areas. This person may also perform Task 2.
- Task 2: Unloads live birds from the shipping cages to the conveyors. This operation is either automated or manual.
- Task 3: Live Hang: Takes live birds from conveyors and hangs them in shackles.
- Task 4: Kill Room Attendant (Backup Killer): Oversees the automatic poultry killing process and kills any birds missed by the machine.
- Task 5: Picking Room Operator: Ensures that equipment (e.g., stunner, scalders, pickers, and conveyors) functions properly.
- Task 6: Paw Room Grader: Sorts and separates product on conveyor.
Task 1: Forklift Operator
The forklift operator uses a forklift to move large catch-cages of poultry from transport trucks to the conveyor dumper system. This process moves from the outside to the inside of the dock area. This person may also perform Task 2.
Hazards of this task may include:
Hazardous Situation
Forklifts are driven in heavily congested areas where many other operations are being performed. Visibility and sightlines can be limited, increasing the chance of collisions between machinery and employees.
Possible Solutions
- Use signs and policies to prohibit others from entering into these areas.
- Use horn when appropriate to alert others.
- Improve lighting where applicable.
- Drive forklift backwards when moving loads.
Hazardous Situation
Over a long period of time the solid rubber wheel on the front of the forklift has developed a flat spot, resulting in unstable loads and poor handling.
Possible Solutions
- Train operators to inspect and recognize potential problems or hazards.
- Implement equipment inspection plan.
- Report and correct problems as soon as identified.
Hazardous Situation
The employee is outside and is exposed to all weather conditions: rain, snow, ice, and heat, resulting in possible slips or falls from working/walking on slippery surfaces.
Possible Solutions
- Provide a roof or cover over forklift operations.
- Reduce slippery surface conditions (e.g., snow removal).
- Wear anti-skid footwear.
Hazardous Situation
Employee must release pull chain to remove chicken cages from trucks, resulting in strains from reaching and possible cuts.
Possible Solutions
- Provide gloves to pad and protect hands.
- Provide ladders or platforms so employee can be repositioned to minimize awkward postures.
- Minimize manual handling of large cages so employees are not exposed to conditions where strains may occur.
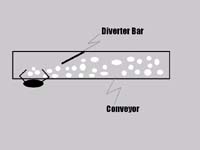
Task 2A: Automatic Dumper Operator
An employee operates the machinery that mechanically dumps live birds from catch-cages. After being removed from cages, the birds are moved by conveyor to the live hang area.
Hazards of this task may include:
Hazardous Situation
Controls may be difficult to manipulate and/or improperly located. This may cause ergonomic stress on the hands, arms, shoulders, and upper back, and may result in injury.
Possible Solutions
- Use gloves to pad the hands.
- Locate controls for ease of use.
- Maintain controls to ensure ease of operation.
Hazardous Situation
Frequent and rapid movement near heavy machinery increases the chance that employees may slip into the machine or be caught by or between moving parts. This is especially true if machinery is outside or exposed to wet or icy conditions.
Possible Solutions
- Follow good housekeeping procedures.
- Properly guard machinery to keep employees away from moving parts.
- Install guardrails around dangerous equipment to prevent injury.
Task 2B: Manual Back Dock Worker

Some facilities still use smaller catch-cages holding 10 to 12 birds each that are normally emptied manually by the back dock worker. Stacks of cages are moved from the truck to the dock area by forklift. Workers then manually lift and remove cages from stacks and empty poultry out of cages. Birds are transported by conveyor from this station to the live hang area.
Hazards of this task may include:
Hazardous Situation
The worker must manually remove cages from stacks, and lift and tilt them to empty chickens from cages. The lifting, bending, and reaching causes stress to the back and shoulders.
Possible Solutions
- Install automatic dumper system.
- Train workers how to lift properly to reduce injury.
- Provide two persons to lift each cage.
- Rotate employees to job with non-lifting task.
Hazardous Situation
As birds are dumped, feather dander and fecal debris may become airborne and inhaled by employees. Diseases associated with handling live chickens and contact with poultry feces and dust include allergic alveolitis, cryptosporadiosis, histoplasmosis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, psittacosis, and Newcastle disease.
Possible Solutions
- Provide back fan ventilation that moves dust and debris away from employees.
- Provide workers with dust respirators and gloves.
- Provide facilities for employees to clean up before eating.
- Train workers to follow prescribed hand washing procedures.
- Follow good housekeeping procedures.
Task 3: Live Hang

Takes live birds from conveyors and hangs them in shackles.
Employees lift live poultry from the supply conveyer and hang the birds by their feet from a shackle conveyor.
Hazards of this task may include:
Hazardous Situation
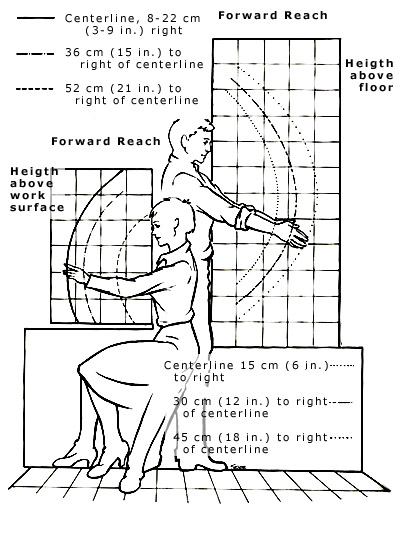
Ergonomic hazards of reaching down to access birds on supply conveyor and reaching up to hang them on the shackle conveyor can lead to shoulder, back, and neck strain because of awkward postures and repetitive motion. The employees at the beginning of the line often work faster than those near the end of the line causing fatigue. Workers stand for long periods of time.
Possible Solutions
- Minimize forward reaches by moving shackle conveyor towards employee.
- Minimize vertical distance between shackles and belt conveyor to reduce lifting of the arms to reach shackle and bending down to reach supply conveyor.
- Rotate employees up and down hanging line to vary the rate at which they perform the task.
- Ramp shackle conveyor down toward the end of the line where there is less interference from birds on supply conveyor.
- Provide height-adjustable stands for shorter employees.
- Provide anti-fatigue mats.
Hazardous Situation
Workers get covered with poultry mess and dust that can expose them to diseases associated with handling live chickens and contact with poultry feces and dust, such as allergic alveolitis, cryptosporidiosis, histoplasmosis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, psittacosis, and Newcastle disease.
Possible Solutions
- Install adequate ventilation systems that would reduce exposure to aerosolized dust. Supply make-up air from behind employee and exhaust from far side of the conveyor.
- Provide proper personal protective equipment and clothing.
- Provide facilities for employees to clean up before eating.
- Train workers to follow prescribed hand washing procedures.
- Follow good housekeeping procedures.
Hazardous Situation
It is difficult for workers to see when lighting is reduced to calm the chickens. This lack of illumination contributes to slips, falls and cuts, and makes inadequately guarded fans even more dangerous.
Possible Solutions
- Install adequate ventilation systems that would reduce exposure to aerosolized dust. Supply make-up air from behind employee and exhaust from far side of the conveyor.
- Provide appropriate light for entry and exit.
- Keep walkways clean and free of debris and obstacles.
- Provide enough space between workers to avoid cuts.
- Make sure all fans both for contamination control and comfort, that are mounted less than 7 feet above the working surface, are adequately guarded.
Hazardous Situation
Standing for a long time can cause pain and strains in the legs and lower back. Common types of footwear worn in this area (e.g. rubber boots) do not provide much arch support.
Possible Solutions
- Install sit/stand stools, which allow employees to lean and have their weight supported while still remaining in an upright posture.
- Install height-adjustable stands so cuts can be performed at mid-chest level.
- Rotate to tasks that do not require prolonged standing.
- Provide shoe insoles that cushion the feet and spread foot pressure over a larger surface.
Task 4: Kill Room Attendant (Backup Killer)

Oversees the automatic poultry killing process and kills any birds missed by the machine.
The kill room attendant monitors the automated poultry killing process and uses a knife to kill any birds missed by the machine.
Hazards of this task may include:
Hazardous Situation
Standing for a long time can cause pain and strains in the legs and lower back. Common types of footwear worn in this area (e.g. rubber boots) do not provide much arch support.
Possible Solutions
- Install sit/stand stools, which allow employees to lean and have their weight supported while still remaining in an upright posture.
- Install height-adjustable stands so cuts can be performed at mid-chest level.
- Rotate to tasks that do not require prolonged standing.
- Provide shoe insoles that cushion the feet and spread foot pressure over a larger surface.
Hazardous Situation
Employee stands in 2-3 inches of blood, which creates slippery floor conditions, resulting in a worker falling while holding a knife.
Possible Solutions
- Provide effective drainage to prevent standing blood.
- Provide rubber boots with high traction soles.
- Sheath knives before entry to and exit from work areas.
Hazardous Situation
During the processing of birds in this area, blood may get in the worker's face and eyes creating a hazard of infection and exposure to disease.
Possible Solutions
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including mesh gloves, face shields, and protective clothing.
- Develop and follow good housekeeping procedures.
Hazardous Situation
Employee is surrounded by equipment and product that may block sightlines where access from and to work areas is restricted. Access points may not be obvious in cases of fire or other emergencies.
Possible Solutions
- Keep exists free and clear at all times.
- Clearly and properly mark exits.
- Implement emergency action plan.
Hazardous Situation
Workers use a knife to perform this cutting task. Factors such as poorly fitting gloves, slick handles, inappropriately sized handles, or dull blades can increase the force that must be used. Minimize repetitive or prolonged exertion of finger force when performing cutting tasks, which can stress the tendons and tendon sheath of the hand.
Possible Solutions
- Keep knives sharp and in good condition.
- Remove damaged knives from service.
- Use knives appropriate for the task.
- Provide properly sized gloves.
- Provide knives with a handle loop so they can remain in hand without the employee actively gripping the handle.
Task 5: Picking Room Operator
Ensures that equipment (e.g., stunner, scalders, pickers, and conveyors) functions properly.
A picking room operator ensures that equipment (e.g., stunner, scalders, pickers, and conveyors) functions properly. Most of the time on the job is spent walking around the equipment, performing a quality assessment of its operation.
Hazards of this task may include:
Hazardous Situation
Workers in wet areas may contact electrical wires causing electrical shock.
Possible Solutions
- Train workers how to recognize electrical hazards.
- Report and correct electrical hazards as soon as they are discovered.
- Schedule preventative maintenance to inspect for frayed or damaged equipment.
- Use appropriate equipment for wet locations.
Hazardous Situation
Employees may need to work around moving and unguarded equipment where an accident may result in possible amputations or strangulation.
Possible Solutions
- Properly guard and regularly maintain machines and equipment.
- Use Lockout/Tagout program.
- Use appropriate equipment for wet locations.
Hazardous Situation
Workers in this area are exposed to high noise levels from the surrounding machinery and processing equipment, which can result in hearing loss.
Possible Solutions
- Provide workers with hearing protection devices and require their use.
- Use belt-driven plucking machines rather than chain-driven machines.
Task 6: Paw Room Grader

Sorts and separates product on conveyor.
The paw room grader inspects and sorts product (feet) on conveyor. This is sometimes used as a light duty position.
Hazards of this task may include:
Hazardous Situation
Standing for a long time reduces blood flow to the legs, forces isolated muscles to work for an extended period of time and increases the risk of fatigue and varicose veins.
Possible Solutions
- Install sit/stand stools, which allow employees to lean and have their weight supported while still remaining in an upright position.
- Rotate to tasks that do not require prolonged standing.
- Provide shoe insoles that cushion the feet and spread foot pressure over a larger surface.
- Provide a foot rest in front of employees so they can shift their posture.
Hazardous Situation
Employees spend a long time looking down at a conveyor belt, which moves product past them. This can cause neck and shoulder pain and potentially carpal tunnel-like symptoms.
Possible Solutions
- Conveyor should be at about elbow height of employee. Provide height-adjustable stands to properly position employees.
- Tilt conveyor toward employee.
- Rotate to other jobs that provide more movement.
- Provide time and training about stretching to relieve neck fatigue.