Evacuation Plans and Procedures eTool
Portable Fire Extinguishers » Extinguisher Placement and Spacing
Portable fire extinguishers can be an effective early response to a developing fire, if they are installed and used properly. In this section, we are going to review general information about the placement and spacing of portable fire extinguishers.
If employees use portable fire extinguishers to fight small fires, they must be installed in all areas of the workplace. To ensure each area is protected properly, ask yourself the following questions:
To avoid putting workers in danger, fire extinguishers should be located throughout the workplace and readily accessible in the event of a fire. [29 CFR 1910.157(c)] You can usually find them in hallways, laundry rooms, meeting rooms, kitchens, mechanical/electrical rooms, and near exit doors.
Selection and Placement:
If employees use portable fire extinguishers, they must be selected and positioned based on the potential type and size of fire that can occur. [29 CFR 1910.157(d)(1)] The following guidelines will help you identify the number and types of portable fire extinguishers you should have.
|
Type of Fire |
Size and Spacing |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class A |
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) recommends that locations such as offices, classrooms, and assembly halls that contain mainly Class A combustible materials have one 2-A extinguisher for every 3,000 square feet. [Standard for Portable Fire Extinguishers (NFPA 10 (2010), Table 6.2.1.1, Fire Extinguisher Size and Placement for Class A Hazards)]. OSHA requires that all employees have access to an extinguisher within 75 feet travel-distance. [29 CFR 1910.157(d)(2)] NOTE: Uniformly spaced standpipe systems or hose stations connected to a sprinkler system for emergency use can be used instead of Class A portable fire extinguishers, if they meet the respective requirements of 29 CFR 1910.158 or 29 CFR 1910.159, provide total coverage of the area to be protected, and employees are trained at least annually in their use. [29 CFR 1910.157(d)(3)] |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Class B |
Locations that contain Class B flammables, such as workshops, storage areas, research operations, garages, warehouses, or service and manufacturing areas requires that all employees have access to an extinguisher within 50 feet travel-distance. [29 CFR 1910.157(d)(4)]
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Class C |
Class C extinguishers are required where energized electrical equipment is used. The extinguisher size and spacing is based on its Class A or B hazard. [29 CFR 1910.157(d)(5)] |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Class D |
Locations where combustible metal powders, flakes, shavings, or similarly sized materials are generated at least once every two weeks must install Class D portable fire extinguishers not more then 75 feet from the hazard. [29 CFR 1910.157(d)(6)] |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Class K |
Locations where potential fire hazards from combustible cooking media (vegetable or animal oils and fats) exist must install Class K extinguishers at a maximum travel distance of 30 feet. [NFPA 10, Standard for Portable Fire Extinguishers. See Section 6.6, Installations for Class K Hazards] |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
For more information on types of extinguishers, see Extinguisher Basics. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Installation:
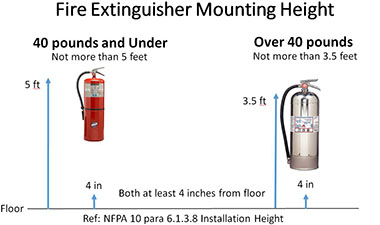
To prevent fire extinguishers from being moved or damaged, they should be mounted on brackets or in wall cabinets with their carrying handles placed 3-1/2 to 5 feet above the floor, depending on the type of extinguisher. Those with gross weights of no more than 40 pounds (lbs.) should be mounted with their carrying handles no higher than 5 feet from the floor. Larger fire extinguishers (over 40 lbs. gross weight) need to be mounted at lower heights, with their carrying handles no more than 3-1/2 feet from the floor. All hand-portable fire extinguishers need to have at least 4 inches of clearance between their bottoms and the floor.
Before installing any portable fire extinguisher, check the label to be sure it is approved by a nationally recognized testing laboratory. [29 CFR 1910.157(c)(2)]
Prohibited Fire Extinguishers:
The following types of portable fire extinguishers are considered dangerous and should not be used:

- Any extinguisher having a shell construction of copper or brass joined by soft solder and/or rivets.
- Any extinguisher that must be turned upside down to rupture a cartridge or to start an uncontrollable pressure generating chemical reaction to expel the agent. [29 CFR 1910.157(c)(5)] This includes:
- Soda acid
- Foam
- Water-cartridge
- Loaded stream cartridge
- Extinguishers that use chlorobromomethane (Halon 1011) or carbon tetrachloride as an extinguishing agent. These agents are toxic and carbon tetrachloride may cause cancer and can produce phosgene gas (used as a chemical weapon during World War I) when used on electrical fires. [29 CFR 1910.157(c)(3)]

Regular maintenance and inspections of your portable fire extinguishers will provide assurance that they will operate effectively and safely if they are needed. [29 CFR 1910.157(c)(4)]
Inspect all extinguishers at least once a month. Use the following checklist as a guide.
- Is each extinguisher in its designated place, clearly visible, and not blocked by equipment, coats or other objects that could interfere with access during an emergency?
- Is the nameplate with operating instructions legible and facing outward?
- Is the pressure gauge showing that the extinguisher is fully charged (the needle should be in the green zone)?
- Is the pin and tamper seal intact?
- Is the extinguisher in good condition and showing no signs of physical damage, corrosion, or leakage?
- Have all dry powder extinguishers been gently rocked top to bottom to make sure the powder is not packing?
NOTE: If you did not answer yes to all of these questions, have the extinguisher fixed or replaced immediately!

