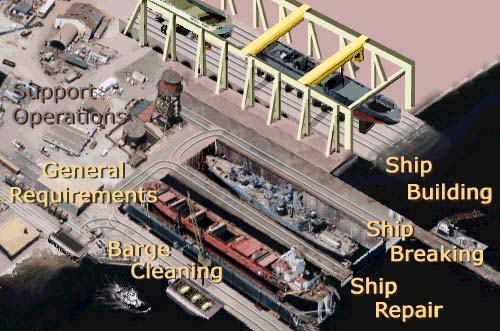
Shipyard Employment eTool
Shipyard Employment
Shipyard work is traditionally hazardous, with an injury-accident rate more than twice that of construction and general industry. OSHA has targeted the industry in its Strategic Plan to reduce injuries and illnesses and prevent fatalities. This eTool describes common hazards and possible solutions for tasks performed during the ship repair process.
This page was developed as a product of the Alliances between OSHA and the American Shipbuilding Association (ASA), National Shipbuilding Research Program (NSRP) and the Shipbuilders Council of America (SCA).
The Fire Protection in Shipyard Employment Standard (29 CFR Part 1915 Subpart P) was issued September 15, 2004 and became effective December 14, 2004. A Fire Protection module has been added to address these changes. In addition, it is anticipated the Ship Repair, Shipbuilding and Shipbreaking eTool modules will be modified in the future to address the Shipyard fire protection standard.
See OSHA's Workers' Rights page for more information on rights and protections.
*eTools are "stand-alone," interactive, Web-based training tools on occupational safety and health topics. They are highly illustrated and utilize graphical menus. As indicated in the disclaimer, eTools do not create new OSHA requirements.