Legionellosis (Legionnaires' Disease and Pontiac Fever)
Overview
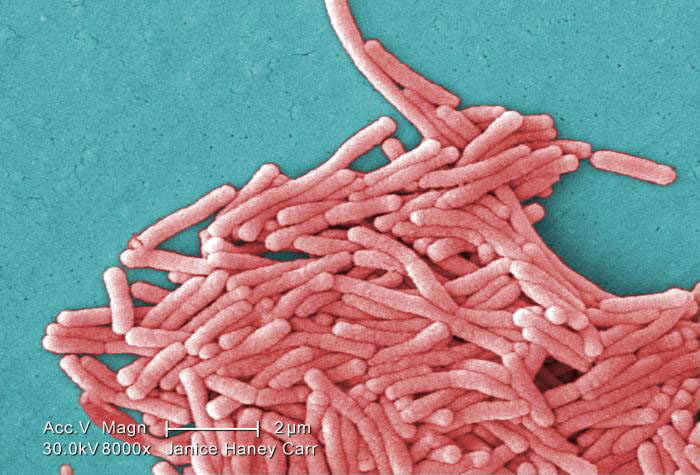
Under a moderately-high magnification of 8000X, this colorized scanning electron microscopic (SEM) image depicts a large grouping of Gram-negative Legionella pneumophila bacteria. These bacteria cause Legionnaires' disease and Pontiac Fever, collectively known as Legionellosis.
Legionnaires' disease and Pontiac Fever are collectively known as Legionellosis, a disease caused by Legionella bacteria. Legionnaires' disease is a serious, potentially deadly, lung infection (i.e., pneumonia); and Pontiac Fever is a less serious infection with milder symptoms similar to the flu (i.e., seasonal influenza). Although Legionella are usually harmless and found naturally in water and soil, it becomes a potentially deadly human health hazard when it grow in places such as poorly maintained domestic and industrial water systems; cooling towers; or heating, ventilation, and air condition (HVAC) systems. Workers may develop Legionellosis if they are exposed to Legionella from these types of sources, especially in water droplets or respirable fine mists small enough to inhale.
Around 6,000 Legionnaires' disease cases are reported each year in the United States. However, scientists believe the reported totals are much lower than the actual cases due in part to the difficulty in distinguishing Legionnaires' disease from other types of pneumonia. The most recent U.S. population-based study estimated that 8,000-18,000 people are hospitalized each year with Legionnaires' disease1. Because patients with Pontiac Fever usually get better on their own, cases may not be routinely recognized or reported.
Managing Legionella and preventing worker exposures and Legionellosis cases depend on implementing an effective water management program. These programs focus on describing water systems and their components, identifying areas where Legionella could grow, deciding where control measures are needed and how to monitor them, planning response actions when control measures fail, and monitoring and documenting water management activities.2 OSHA developed this Safety and Health Topics page to increase awareness about Legionella hazards and help employers plan and implement water management programs for controlling potential Legionella sources. Various elements of water management programs and recommendations are available
Background
Provides historic information about Legionellosis, routes of disease transmission, the different Legionella species, and habitats.
Hazard Recognition
Talks about Legionella exposure and infection risk. Conditions that promote Legionella growth, water systems most susceptible to Legionella contamination, and how to determine if Legionella are in water systems.
Medical Information
Describes Legionnaires' disease and Pontiac Fever signs and symptoms, as well as diagnosis and medical management.
Standards
Related OSHA standards, letters of interpretation, directives, and other regulatory requirements that may apply to workplace exposure to Legionella.
Control and Prevention
Guidance on preventing Legionella growth in manmade water systems through proper facility maintenance. Prevention focuses on design considerations, operations, proper maintenance schedules, and other controls to prevent Legionella growth in systems including, but not limited to, cooling towers, and HVAC systems.
Outbreak Response
Actions necessary to prevent worker exposure during remediation activities.
Additional Resources
Links to OSHA resources on Legionellosis and Legionella, as well as resources from other federal agencies, states, international agencies, non-profit organizations, and peer-reviewed journal articles.
Highlights
- Airborne exposure to environmental sources of Legionella can cause disease, especially in older and immunocompromised people.
- Improperly maintained water systems, such as domestic or industrial water systems or large HVAC systems, are among the leading sources of worker exposure to the bacteria that cause Legionnaires' disease.
- Legionnaires' disease is treatable with antibiotics.
- Legionnaires'; disease is a serious condition with a 10-percent death rate.1
- Illnesses usually occur in the summer and early fall, but Legionnaires' disease can happen in any season.2
- Legionnaires' disease is not contagious. Workers cannot catch Legionnaires' disease from someone else and cannot make someone else sick if they have it.
1 Legionellosis Fact Sheet. World Health Organization (2016).
2 About Legionnaires' Disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
1 Legionellosis - United States, 2000—2009. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 60(32), 1083-1086 (2011).
2 Developing a Water Management Program to Reduce Legionella Growth and Spread in Buildings: A Practical Guide to Implementing Industry Standards. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (2017).

